hadoop编程实例
MapReduce 编程规范
用户编写的程序分成三个部分:Mapper、Reducer 和 Driver。
1.Mapper阶段
(1)用户自定义的Mapper要继承自己的父类
(2)Mapper的输入数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
p.s. K是这一行的偏移量,V是这一行的内容。
(3)Mapper中的业务逻辑写在map()方法中
(4)Mapper的输出数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义) (5)map()方法(MapTask进程)对每一个
2.Reducer阶段
(1)用户自定义的Reducer要继承自己的父类
(2)Reducer的输入数据类型对应Mapper的输出数据类型,也是KV (3)Reducer的业务逻辑写在reduce()方法中
(4)ReduceTask进程对每一组相同k的
3.Driver阶段
相当于YARN集群的客户端,用于提交我们整个程序到YARN集群,提交的是封装了MapReduce程序相关运行参数的job对象
wordcount实例
WordCount.java
package com.shujia.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*
打包代码发送到虚拟机上进行运行
com.shujia.mr.wordcount.WordCount为driver阶段的包路径
执行jar包的命令
hadoop jar hadoop-1.0.jar com.shujia.mr.wordcount.WordCount
查看结果
hdfs dfs -cat /api/out/wordCount/part-r-00000
*/
// 该对象表示一个任务的执行对象
// 需要提供 Configuration对其进行填入配置参数
// jobName用于对当前任务进行赋予名称 => Yarn平台可以展示
// public static Job getInstance(Configuration conf, String jobName)
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "My First Word Count ");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 输入的数据地址 及输出数据的地址 => 使用HDFS上的路径
// org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output. 注意选择该包路径下的
// FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,new Path("/api/data/words.txt"));
// FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("/api/out/wordCount"));
/*
代码优化:
1.输入路径不存在,需要提示 并且抛出异常
2.输出路径已经存在,那么需要代码自动删除
*/
// HDFS路径
// Path inputPath = new Path("/api/data/words.txt");
// Path outputPath = new Path("/api/out/wordCount");
// 本地路径
Path inputPath = new Path("C:\\Users\\19783\\IdeaProjects\\bigdate28_1\\hadoop\\data\\words.txt");
Path outputPath = new Path("C:\\Users\\19783\\IdeaProjects\\bigdate28_1\\hadoop\\data\\out\\wordCount");
// 由于数据在HDFS中,于是可以使用FileSystem对象进行操作
// 当代码打成Jar包 提交到Yarn平台上运行 可以通过Yarn获取到其配置信息
// 获取方式是通过 hdfs的classpath获取
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
WordCountMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
自定义Mapper类需要继承Mapper 该Mapper需要给定4个泛型
public class stuMapper
KEYIN: 输入数据的Key类型 存储的数据是 偏移量(指数据读取的开始位置也表示之前读取到哪个长度) 使用长整型 Java中为Long
由于Hadoop内部实现了一套自己的数据表达式方式 Writable ,所有的Java类型都有其对应的 Hadoop数据类型
Java中为Long => LongWritable
VALUEIN: 表示输入数据的Value类型 存储的是一行数据 Java中为String 字符串
Java中为String 字符串 => Text
输出的数据类型需要根据 计算逻辑推算得到
Mapper阶段的计算逻辑:
1.拿到一行字符串数据Value
2.将Value进行按空格切分
3.将切分后的数据遍历得到每个单词
4.对每个单词作为Key 拼接一个 Value 1
根据上述的逻辑:
KEYOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Key类型 => 单词 => 字符串 => Java中使用String => Hadoop中使用 Text
VALUEOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Value类型 => 1 => 整型 => Java中使用 int => IntWritable
注意:导入类时不要选错包 org.apache.hadoop.io 包路径下
*/
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper
/**
* 需要重写map方法,在该方法中可以实现Mapper端的计算逻辑
*
* @param key 输入的数据的Key => 偏移量 => 读取数据的长度位置
* @param value 读取的一行数据 : hello world
* @param context 表示会话 用于连接Mapper端和Reducer端 形成一个整体
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper
// Text是Hadoop中的数据类型 提供了哪些方法?
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
// TODO 遍历每个单词
for (String word : words) {
// TODO 需要将 word 作为Key 1作为Value写出结果
// 1. word => String类型 要求输出类型为 Text 如何转换 ?
// 2. 1 => int类型 要求输出类型为 IntWritable 如何转换 ?
// 3. 当前Map方法没有返回值 如何将数据写出?
Text outKey = new Text(word);
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(1);
// 通过调用 context.write 可以将数据写出到Reducer阶段
context.write(outKey, outValue);
}
}
}
WordCountReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
Reducer阶段主要是对数据进行做汇总操作
自定义Reducer类需要继承Reducer抽象类 需要提供四个泛型
public class Reducer
KEYIN, VALUEIN: 输入数据的Key和Value的类型 => 是Mapper阶段输出的 Text, IntWritable
Reducer阶段的计算逻辑:
1.接受Mapper端的数据
2.将相同单词所有的Value进行累加
3.将累加后的单词作为Key 单词数和作为Value 写出
KEYOUT, VALUEOUT: 表示Reducer阶段经过逻辑计算后输出的结果
KEYOUT => 单词 => Text
VALUEOUT => 总和 => IntWritable
*/
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer
/**
* reduce方法中可以定义用户的聚合的处理逻辑
*
* @param key 一个单词 hello
* @param values 类型:Iterable
* @param context 上下文对象 可以连接Mapper和Reducer
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable oneValue : values) {
int intValue = oneValue.get(); // intValue => 1
sum += intValue;
}
// TODO 累加完成 需要将数据写出到HDFS或其他地方
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(sum);
context.write(key,outValue);
}
}
MapReduce Join操作(reducer join)
将student.txt和score.txt内容合并
JoinMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import java.io.IOException;
public class JoinMapper extends Mapper
String filename=null;
// 当前setup函数会在每个MapTask任务一开始启动会执行一次
@Override
protected void setup(Mapper
//获取当前处理的切片所属的文字名字
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
filename = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper
String oneLine=value.toString();
/*
1500100003,单乐蕊,22,女,理科六班
1500100004,葛德曜,24,男,理科三班
*/
if (filename.contains("students.txt")){
String[] split = oneLine.split(",");
if (split.length==5){
String id= split[0];
String name=split[1];
String age=split[2];
String gender=split[3];
String clazz=split[4];
context.write(new Text(id),new Text("student#"+name+","+age+","+gender+","+clazz));
}
}else {
//处理成绩
String[] split = oneLine.split(",");
if (split.length==3){
String id=split[0];
String glass = split[1];
String score = split[2];
context.write(new Text(id),new Text("score#"+score));
}
}
}
}
JoinReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class JoinReducer extends Reducer
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
// 用于分开存储学生和成绩信息的列表
List
List
int score_total=0;
// 遍历值,并根据前缀("student#"或"score#")将信息分开
for (Text value : values) {
String[] parts = value.toString().split("#", 2);
if (parts.length == 2) {
String type = parts[0];
String data = parts[1];
if ("student".equals(type)) {
studentInfoList.add(data);
} else if ("score".equals(type)) {
scoreList.add(data);
}
}
}
// 学生信息和总分
if (!studentInfoList.isEmpty() && !scoreList.isEmpty()) {
for (String studentInfo : studentInfoList) {
for (String score : scoreList) {
score_total+=Integer.parseInt(score);
}
context.write(key, new Text(studentInfo + "," + score_total));
}
}
/*如果存在相同ID的学生信息和成绩信息,则进行合并
if (!studentInfoList.isEmpty() && !scoreList.isEmpty()) {
for (String studentInfo : studentInfoList) {
for (String score : scoreList) {
context.write(key, new Text(studentInfo + "," + score));
}
}
}
*/
}
}
JoinDriver.java
package com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class JoinDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "stu ");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(JoinDriver.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(JoinMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(JoinReducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// 本地路径
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/stu");
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/join/stu");
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
或者
ReduceJoinMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.reduce.join;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReduceJoinMapper extends Mapper
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper
// value: 1.总分 2.基本信息数据
String oneLine = value.toString();
if (oneLine.contains(",")) {
// 学生基本信息 1500100006,边昂雄,21,男,理科二班
String[] split = oneLine.split(",");
if (split.length == 5) {
// 将数据写出
context.write(new Text(split[0]), new Text(split[1] + "," + split[2] + "," + split[3] + "," + split[4]));
}
} else if (oneLine.contains("\t")) {
// 学生总分数据 1500100003 359
String[] splitCol = oneLine.split("\t");
if (splitCol.length == 2) {
context.write(new Text(splitCol[0]), new Text(splitCol[1]));
}
}
}
}
ReduceJoinReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.reduce.join;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
public class Reducer
*/
public class ReduceJoinReducer extends Reducer
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
// values : 1.总分 2.信息
String info = "null,null,null,null";
String score = "0";
for (Text value : values) {
String oneValue = value.toString();
if (oneValue.contains(",")) {
// 判断出该数据是基本信息
info = oneValue;
} else {
// 总分
score = oneValue;
}
}
// TODO 拼接数据再写出
context.write(key, new Text(info + "," + score));
}
}
ReduceJoinDriver.java
package com.shujia.mr.reduce.join;
import com.shujia.mr.count.score.CountDriver;
import com.shujia.mr.count.score.CountMapper;
import com.shujia.mr.count.score.CountReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReduceJoinDriver {
/*
需求: 将统计过的学生总分 和 学生基本信息进行关联 得到每个学生的基本信息以及总分数据
TODO:
1.需要使用MapReduce将两份数据加载到集群中进计算
2.数据加载后需要到Mapper阶段进行处理 -> 执行Map方法 -> 每一行执行一次 (每一行有两种数据:1.总分 2.基本信息)
那么需要在Map方法中根据数据的特征将数据区分开
3.选择关联字段学生ID作为Key 其他信息(1.总分 2.基本信息)作为Value输出
4.在Reducer端需要接收相同学生ID的所有数据 对应values有两种数据,1.总分 2.基本信息
5. 对于相同学生ID的两个数据进行判断 对数据进行拼接处理
6. 最终以学生ID作为Key 其他信息拼接作为Value
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
//构建Job对象
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(CountDriver.class);
job.setJobName("Reduce Join");
job.setMapperClass(ReduceJoinMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(ReduceJoinReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// 设置输入输出路径
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/reduce_join");
// Path inputPath = new Path("/data/reduce_join");
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(inputPath+"路径不存在");
}
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/reduce_join");
// Path outputPath = new Path("/data/out/count");
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)){
fileSystem.delete(outputPath,true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath);
// 提交job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
MapReduce Top3操作(亦可以演变排序)
将上一个案例获得文件信息为学生信息加总分,进行排序获得每个班级的前三名
Top3Mapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.stutop3;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Top3Mapper extends Mapper
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper
String oneLine = value.toString();
/*
1500100015 宦怀绿,21,女,理科一班,309
1500100016 null,null,null,null,359
*/
String[] split = oneLine.split("\t");
String id = split[0];
String info = split[1];
String[] infoSplit = info.split(",");
String clazz = infoSplit[3];
// 对班级信息进行判断
if (!clazz.equals("null")){
context.write(new Text(clazz),value);
}
}
}
Top3Reducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.stutop3;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Top3Reducer extends Reducer
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
// key 班级信息
// values 表示一个班级所有的学生数据
ArrayList
for (Text value : values) {
String oneLine = value.toString();
// 1500100013 逯君昊,24,男,文科二班,369 数据切分
String[] split = oneLine.split("\t");
String[] infoSplit = split[1].split(",");
// TODO:由于需要将数据保存到List中,之后再去对数据进行排序
// 需要将数据包装成对象再添加对象到List 再使用对象进行排序
Student student = new Student(split[0], infoSplit[0], Integer.parseInt(infoSplit[1]), infoSplit[2], infoSplit[3], Integer.parseInt(infoSplit[4]));
oneClazzAllStu.add(student);
}
Collections.sort(oneClazzAllStu, new Comparator
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o2.score - o1.score;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Student student = oneClazzAllStu.get(i);
context.write(new Text(student.toString()),NullWritable.get());
}
}
static class Student {
String id;
String name;
int age;
String gender;
String clazz;
int score;
public Student(String id, String name, int age, String gender, String clazz, int score) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.clazz = clazz;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id +","+name+","+age+","+gender+","+clazz+","+score;
}
}
}
Top3Driver.java
package com.shujia.mr.stutop3;
import com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore.JoinDriver;
import com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore.JoinMapper;
import com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore.JoinReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class Top3Driver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "stuTop3 ");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(Top3Driver.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(Top3Mapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(Top3Reducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// 本地路径
Path inputPath = new Path("data/out/join/stu/part-r-00000");
Path outputPath = new Path("data/out/join/stuTop");
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
MapReduce 计数操作
对于每个班级学生进行男女人数统计
stuMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.stugender;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class stuMapper extends Mapper
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper
String oneLine = value.toString();
/*
1500100001 施笑槐,22,女,文科六班,406
1500100002 吕金鹏,24,男,文科六班,440
1500100003 单乐蕊,22,女,理科六班,359
*/
String[] spilt=oneLine.split("\t");
String gender=spilt[1].split(",")[2];
String clazz=spilt[1].split(",")[3];
context.write(new Text(clazz),new Text(gender));
}
}
stuReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.stugender;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class stuReducer extends Reducer
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
int male=0;
int man=0;
for (Text value : values) {
String oneLine = value.toString();
if (oneLine.equals("男")){
man+=1;
}else {
male+=1;
}
}
context.write(key, new Text("男: " + man + ", 女: " + male));
}
}
stuDriver.java
package com.shujia.mr.stugender;
import com.shujia.mr.stutop3.Top3Driver;
import com.shujia.mr.stutop3.Top3Mapper;
import com.shujia.mr.stutop3.Top3Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class stuDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "stu ");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(stuDriver.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(stuMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(stuReducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// 本地路径
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/join/stu/part-r-00000");
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/stu2");
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
MapReduce 分区操作(Partitioner)
将每个班级成绩按班级分别输出到不同的文件,要进行分区操作
PartitionerMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class PartitionerMapper extends Mapper
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper
String oneLine = value.toString();
String[] split = oneLine.split("\t");
/*
1500100001 施笑槐,22,女,文科六班,406
1500100002 吕金鹏,24,男,文科六班,440
*/
String id=split[0];
String info=split[1];
String clazz= info.split(",")[3];
String name=info.split(",")[0];
String age=info.split(",")[1];
String score=info.split(",")[4];
context.write(new Text(clazz),new Text(id+","+name+","+age+","+score+","+clazz));
}
}
PartitionerReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class PartitionerReducer extends Reducer
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
TreeSet
for (Text value : values) {
String oneLine = value.toString();
// 1500100001,施笑槐,22,406
String id=oneLine.split(",")[0];
String name=oneLine.split(",")[1];
String age=oneLine.split(",")[2];
int score=Integer.parseInt(oneLine.split(",")[3]);
String clazz=oneLine.split(",")[4];
Stu stu = new Stu(id,name,age,score,clazz);
String string = key.toString();
set.add(stu);
}
for (Stu stu1 : set) {
context.write(new Text(String.valueOf(stu1)),NullWritable.get());
}
}
static class Stu implements Comparable
String id;String name;String age;int score;String clazz;
public Stu(String id, String name, String age, int score,String clazz) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
this.clazz=clazz;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Stu o) {
return o.score-this.score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id+","+name+","+age+","+score+","+clazz;
}
}
}
MyPartitioner.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner
@Override
public int getPartition(Text text, Text text2, int i) {
String key = text.toString();
switch (key) {
case "文科一班":
return 0;
case "文科二班":
return 1;
case "文科三班":
return 2;
case "文科四班":
return 3;
case "文科五班":
return 4;
case "文科六班":
return 5;
case "理科一班":
return 6;
case "理科二班":
return 7;
case "理科三班":
return 8;
case "理科四班":
return 9;
case "理科五班":
return 10;
default:
return 11;
}
}
}
PartitionerDriver.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitioner;
import com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore.JoinDriver;
import com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore.JoinMapper;
import com.shujia.mr.stujoinscore.JoinReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class PartitionerDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "clazz");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(PartitionerDriver.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(PartitionerMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(PartitionerReducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
//将Reduce任务的数量设置为12。这意味着在作业执行期间,将会有12个Reduce任务并行地处理输入数据,并生成12个输出文件。
job.setNumReduceTasks(12);
// 本地路径
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/join/stu/part-r-00000");
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/partitioner");
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
注意事项:
如果您只设置了 `job.setNumReduceTasks(12)`,但没有定义分区器(Partitioner),则默认的分区器将被使用。默认的分区器会将键(Key)按照哈希函数进行分区,将相同哈希值的键分配给同一个Reduce任务。
这意味着,如果您没有自定义分区器,并且只设置了 `job.setNumReduceTasks(12)`,则作业将会使用默认的哈希分区器,并将键的哈希值决定它们被分配到哪个Reduce任务中。
但是需要注意的是,如果您的键没有良好的分布特性,或者某些键的哈希值冲突较多,那么默认的哈希分区器可能会导致不均匀的数据分布和不理想的性能。在这种情况下,您可能需要自定义分区器,以根据键的特性将数据更均匀地分配到不同的Reduce任务中。
MapReduce 小文件合并操作
当MapReduce的数据源中小文件过多,那么根据FileInputFormat类中GetSplit函数加载数据,会产生大量的切片从而启动过多的MapTask任务,MapTask启动过多那么会导致申请过多资源,并且MapTask启动较慢,执行过程较长,效率较低
如何解决? 可以使用MR中的CombineTextInputFormat类,在形成数据切片时,可以对小文件进行合并
WordCountMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
自定义Mapper类需要继承Mapper 该Mapper需要给定4个泛型
public class Mapper
KEYIN: 输入数据的Key类型 存储的数据是 偏移量(指数据读取的开始位置也表示之前读取到哪个长度) 使用长整型 Java中为Long
由于Hadoop内部实现了一套自己的数据表达式方式 Writable ,所有的Java类型都有其对应的 Hadoop数据类型
Java中为Long => LongWritable
VALUEIN: 表示输入数据的Value类型 存储的是一行数据 Java中为String 字符串
Java中为String 字符串 => Text
输出的数据类型需要根据 计算逻辑推算得到
Mapper阶段的计算逻辑:
1.拿到一行字符串数据Value
2.将Value进行按空格切分
3.将切分后的数据遍历得到每个单词
4.对每个单词作为Key 拼接一个 Value 1
根据上述的逻辑:
KEYOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Key类型 => 单词 => 字符串 => Java中使用String => Hadoop中使用 Text
VALUEOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Value类型 => 1 => 整型 => Java中使用 int => IntWritable
注意:导入类时不要选错包 org.apache.hadoop.io 包路径下
*/
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper
/**
* 需要重写map方法,在该方法中可以实现Mapper端的计算逻辑
*
* @param key 输入的数据的Key => 偏移量 => 读取数据的长度位置
* @param value 读取的一行数据 : hello world
* @param context 表示会话 用于连接Mapper端和Reducer端 形成一个整体
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper
// Text是Hadoop中的数据类型 提供了哪些方法?
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
// TODO 遍历每个单词
for (String word : words) {
// TODO 需要将 word 作为Key 1作为Value写出结果
// 1. word => String类型 要求输出类型为 Text 如何转换 ?
// 2. 1 => int类型 要求输出类型为 IntWritable 如何转换 ?
// 3. 当前Map方法没有返回值 如何将数据写出?
Text outKey = new Text(word);
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(1);
// 通过调用 context.write 可以将数据写出到Reducer阶段
context.write(outKey, outValue);
}
}
}
WordCountReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
Reducer阶段主要是对数据进行做汇总操作
自定义Reducer类需要继承Reducer抽象类 需要提供四个泛型
public class Reducer
KEYIN, VALUEIN: 输入数据的Key和Value的类型 => 是Mapper阶段输出的 Text, IntWritable
Reducer阶段的计算逻辑:
1.接受Mapper端的数据
2.将相同单词所有的Value进行累加
3.将累加后的单词作为Key 单词数和作为Value 写出
KEYOUT, VALUEOUT: 表示Reducer阶段经过逻辑计算后输出的结果
KEYOUT => 单词 => Text
VALUEOUT => 总和 => IntWritable
*/
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer
/**
* reduce方法中可以定义用户的聚合的处理逻辑
*
* @param key 一个单词 hello
* @param values 类型:Iterable
* @param context 上下文对象 可以连接Mapper和Reducer
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable oneValue : values) {
int intValue = oneValue.get(); // intValue => 1
sum += intValue;
}
// TODO 累加完成 需要将数据写出到HDFS或其他地方
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(sum);
context.write(key,outValue);
}
}
WordCount.java
package com.shujia.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineFileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineTextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*
执行jar包的命令
hadoop jar hadoop-1.0.jar com.shujia.mr.wordcount.WordCount
*/
// 该对象表示一个任务的执行对象
// 需要提供 Configuration对其进行填入配置参数
// jobName用于对当前任务进行赋予名称 => Yarn平台可以展示
// public static Job getInstance(Configuration conf, String jobName)
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// conf.set("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize","1048576");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "My First Word Count ");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 输入的数据地址 及输出数据的地址 => 使用HDFS上的路径
// org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output. 注意选择该包路径下的
// FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,new Path("/api/data/words.txt"));
// FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("/api/out/wordCount"));
/*
代码优化:
1.输入路径不存在,需要提示 并且抛出异常
2.输出路径已经存在,那么需要代码自动删除
*/
// HDFS路径
// Path inputPath = new Path("/api/data/words.txt");
// Path outputPath = new Path("/api/out/wordCount");
// 本地路径
// Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/words.txt");
// 直接给定一个目录
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/wordcount");
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/wordCount");
// 由于数据在HDFS中,于是可以使用FileSystem对象进行操作
// 当代码打成Jar包 提交到Yarn平台上运行 可以通过Yarn获取到其配置信息
// 获取方式是通过 hdfs的classpath获取
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(job.getConfiguration());
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
// 设置ReduceTask的数量
job.setNumReduceTasks(3);
// 设置小文件合并
job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class);
// 设置切片的大小
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job,20 * 1024 * 1024L); // 调小
// CombineTextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(); //调大
// 小文件切分合并的逻辑
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
注意:
在上述代码片段中,使用了`CombineTextInputFormat`来合并小文件。`CombineTextInputFormat`是一种输入格式,它可以将多个小文件合并成一个切片进行处理,以提高作业的执行效率。
在设置`CombineTextInputFormat`时,可以使用以下两个方法来调整切片的大小:
1. `CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, maxSize)`:设置切片的最大大小。这个值用来限制一个切片的最大字节数。如果一个文件的大小超过了这个值,它将被拆分成多个切片。`maxSize`参数的单位是字节。
2. `CombineTextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(job, minSize)`:设置切片的最小大小。这个值用来限制一个切片的最小字节数。如果一个文件的大小小于这个值,它将不会被拆分成切片。`minSize`参数的单位是字节。
根据您的需求,您可以根据实际情况调整这两个值。如果您希望更小的切片大小,可以减小`setMaxInputSplitSize()`的参数值;如果您希望更大的切片大小,可以增大`setMinInputSplitSize()`的参数值。
请注意,切片的大小设置会影响作业的执行效率和数据处理的粒度。选择适当的切片大小可以提高作业的性能,但也需要考虑到集群的资源利用和数据处理的负载均衡等因素。
输出类及其自定义
OutputFormat是MapReduce输出的基类,所有实现MapReduce输出都实现了OutputFormat接口。默认输出格式是TextOutputFormat
当需要输出数据到MySQL/HBase/Elasticsearch等存储框架时需要自定义OutputFormat。
定义OutputFormat步骤:
1.自定义一个类继承FileOutputFormat
2.改写RecordWriter,具体改写输出数据的方法wtite()
MyRecordWriter.java
package com.shujia.mr.output;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class MyRecordWriter extends RecordWriter
TaskAttemptContext job;
FileSystem fileSystem;
BufferedWriter more450BufferedWriter;
BufferedWriter less450BufferedWriter;
/*
在该方法中可以拿到 最终要输出的Key Value 数据
数据写出要使用IO流 => 使用FileSystem对象进行操作 => 通过create方法创建输出流 => 数据写出
TODO:
1.在该类中定义job的一个属性
2.通过 构造方法可以将 MyOutputFormat 中的job对象传入
3.通过job对象 获取配置类创建FileSystem对象 将该FileSystem对象作为其中的一个属性
*/
public MyRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job, Path more450Path,Path less450Path) {
this.job = job;
Configuration configuration = job.getConfiguration();
try {
// 按照不同的需求定义IO输出流
fileSystem = FileSystem.get(configuration);
// 对文件不存在的需要进行创建
if (!fileSystem.exists(more450Path.getParent())) {
fileSystem.mkdirs(more450Path.getParent());
}
if (!fileSystem.exists(less450Path.getParent())) {
fileSystem.mkdirs(less450Path.getParent());
}
FSDataOutputStream more450fsDataOutputStream = fileSystem.create(more450Path);
more450BufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(more450fsDataOutputStream));
FSDataOutputStream less450fsDataOutputStream = fileSystem.create(less450Path);
less450BufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(less450fsDataOutputStream));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void write(Text key, NullWritable value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String oneLine = key.toString();//1500100001 施笑槐,22,女,文科六班,406
String[] split = oneLine.split("\t");
String stu = split[1];
String[] split1 = stu.split(",");
if (split1.length == 5){
// 1500100009,沈德昌,21,男,理科一班,251
int score = Integer.parseInt(split1[4]);
if (score >=450){
more450BufferedWriter.write(oneLine);
more450BufferedWriter.newLine();
more450BufferedWriter.flush();
}else {
less450BufferedWriter.write(oneLine);
less450BufferedWriter.newLine();
less450BufferedWriter.flush();
}
}
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
more450BufferedWriter.close();
less450BufferedWriter.close();
fileSystem.close();
}
}
MyOutputFormat.java
package com.shujia.mr.output;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.OutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Progressable;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat
/**
* 该方法要求返回一个RecordWriter的对象,该对象是用于 按照一定规则写出数据
* 需要再定义一个RecordWriter的子类,在该子类中 进行编写自定义输出逻辑
* @param job the information about the current task.
* @return
*/
@Override
public RecordWriter getRecordWriter( TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException {
// URI[] cacheFiles = job.getCacheFiles();
// new Path("hadoop/data/out/output/more450.txt").toUri(),
// new Path("hadoop/data/out/output/less450.txt").toUri(),
return new MyRecordWriter(job,new Path("hadoop/data/out/output/more450.txt")
,new Path("hadoop/data/out/output/less450.txt"));
// return new MyRecordWriter(job,new Path(cacheFiles[0]),new Path(cacheFiles[1]));
}
}
OutputMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.output;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
TODO:
将Reducejoin的结果数据按分数大于450分的保存到一个文件中
,小于450分的数据再写入另外一个文件中
Mapper中需要读取ReduceJoin的数据,直接将数据写出 由自定义的输出类对数据分数进行判断,再写出到不同的文件中
*/
public class OutputMapper extends Mapper
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper
context.write(value,NullWritable.get());
}
}
OutputDriver.java
package com.shujia.mr.output;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class OutputDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(OutputDriver.class);
job.setJobName("output");
job.setMapperClass(OutputMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// 最终输出的就是Mapper端输出的
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// 设置自定义输出类
job.setOutputFormatClass(MyOutputFormat.class);
// 设置输入输出路径
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/join/stu/part-r-00000");
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(inputPath+"路径不存在");
}
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/output");
// Path outputPath = new Path("/data/out/count");
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)){
fileSystem.delete(outputPath,true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath);
// 提交job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
分区及其自定义
PartitionerMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitionermu;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class PartitionerMapper extends Mapper
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper
String oneLine = value.toString();
String[] split = oneLine.split("\t");
/*
1500100001 施笑槐,22,女,文科六班,406
1500100002 吕金鹏,24,男,文科六班,440
*/
String id=split[0];
String info=split[1];
String clazz= info.split(",")[3];
String name=info.split(",")[0];
String age=info.split(",")[1];
String score=info.split(",")[4];
context.write(new Text(clazz),new Text(id+","+name+","+age+","+score+","+clazz));
}
}
PartitionerReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitionermu;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.MultipleOutputs;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class PartitionerReducer extends Reducer
/**
* 设置多个文件输出
* */
private MultipleOutputs mos;
@Override
protected void setup(Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
mos=new MultipleOutputs(context);//初始化mos
}
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
TreeSet
for (Text value : values) {
String oneLine = value.toString();
// 1500100001,施笑槐,22,406
String id=oneLine.split(",")[0];
String name=oneLine.split(",")[1];
String age=oneLine.split(",")[2];
int score=Integer.parseInt(oneLine.split(",")[3]);
String clazz=oneLine.split(",")[4];
Stu stu = new Stu(id,name,age,score,clazz);
String string = key.toString();
set.add(stu);
}
for (Stu stu1 : set) {
switch (stu1.clazz) {
case "文科一班":
mos.write("wk1", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "文科二班":
mos.write("wk2", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "文科三班":
mos.write("wk3", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "文科四班":
mos.write("wk4", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "文科五班":
mos.write("wk5", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "文科六班":
mos.write("wk6", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "理科一班":
mos.write("lk1", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "理科二班":
mos.write("lk2", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "理科三班":
mos.write("lk3", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "理科四班":
mos.write("lk4", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
case "理科五班":
mos.write("lk5", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
default:
mos.write("lk6", stu1.toString(), NullWritable.get());
break;
}
}
}
@Override
protected void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
mos.close();//释放资源
}
static class Stu implements Comparable
String id;String name;String age;int score;String clazz;
public Stu(String id, String name, String age, int score,String clazz) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
this.clazz=clazz;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Stu o) {
return o.score-this.score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id+","+name+","+age+","+score+","+clazz;
}
}
}
MyPartitioner.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitionermu;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner
@Override
public int getPartition(Text text, Text text2, int i) {
String key = text.toString();
switch (key) {
case "文科一班":
return 0;
case "文科二班":
return 1;
case "文科三班":
return 2;
case "文科四班":
return 3;
case "文科五班":
return 4;
case "文科六班":
return 5;
case "理科一班":
return 6;
case "理科二班":
return 7;
case "理科三班":
return 8;
case "理科四班":
return 9;
case "理科五班":
return 10;
default:
return 11;
}
}
}
PartitionerDriver.java
package com.shujia.mr.stuPartitionermu;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.LazyOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.MultipleOutputs;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
public class PartitionerDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "clazz");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(PartitionerDriver.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(PartitionerMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(PartitionerReducer.class);
/**
* 注意在初始化时需要设置输出文件的名
* 另外名称,不支持中文名,仅支持英文字符
*
* **/
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "wk1", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "wk2", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "wk3", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "wk4", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "wk5", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "wk6", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "lk1", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "lk2", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "lk3", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "lk4", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "lk5", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
MultipleOutputs.addNamedOutput(job, "lk6", TextOutputFormat.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class);
//使用上述会产生默认的空文件【part-*-00000】
//通过此配置可以不再产生默认的空文件【part-*-00000】
LazyOutputFormat.setOutputFormatClass(job, TextOutputFormat.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(12);
// 本地路径
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/join/stu/part-r-00000");
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/partitioner_s");
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
结果:
Compress压缩操作
WordCountMapper.java
package com.shujia.mr.compress;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
自定义Mapper类需要继承Mapper 该Mapper需要给定4个泛型
public class Mapper
KEYIN: 输入数据的Key类型 存储的数据是 偏移量(指数据读取的开始位置也表示之前读取到哪个长度) 使用长整型 Java中为Long
由于Hadoop内部实现了一套自己的数据表达式方式 Writable ,所有的Java类型都有其对应的 Hadoop数据类型
Java中为Long => LongWritable
VALUEIN: 表示输入数据的Value类型 存储的是一行数据 Java中为String 字符串
Java中为String 字符串 => Text
输出的数据类型需要根据 计算逻辑推算得到
Mapper阶段的计算逻辑:
1.拿到一行字符串数据Value
2.将Value进行按空格切分
3.将切分后的数据遍历得到每个单词
4.对每个单词作为Key 拼接一个 Value 1
根据上述的逻辑:
KEYOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Key类型 => 单词 => 字符串 => Java中使用String => Hadoop中使用 Text
VALUEOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Value类型 => 1 => 整型 => Java中使用 int => IntWritable
注意:导入类时不要选错包 org.apache.hadoop.io 包路径下
*/
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper
/**
* 需要重写map方法,在该方法中可以实现Mapper端的计算逻辑
*
* @param key 输入的数据的Key => 偏移量 => 读取数据的长度位置
* @param value 读取的一行数据 : hello world
* @param context 表示会话 用于连接Mapper端和Reducer端 形成一个整体
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper
// Text是Hadoop中的数据类型 提供了哪些方法?
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
// TODO 遍历每个单词
for (String word : words) {
// TODO 需要将 word 作为Key 1作为Value写出结果
// 1. word => String类型 要求输出类型为 Text 如何转换 ?
// 2. 1 => int类型 要求输出类型为 IntWritable 如何转换 ?
// 3. 当前Map方法没有返回值 如何将数据写出?
Text outKey = new Text(word);
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(1);
// 通过调用 context.write 可以将数据写出到Reducer阶段
context.write(outKey, outValue);
}
}
}
WordCountReducer.java
package com.shujia.mr.compress;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
Reducer阶段主要是对数据进行做汇总操作
自定义Reducer类需要继承Reducer抽象类 需要提供四个泛型
public class Reducer
KEYIN, VALUEIN: 输入数据的Key和Value的类型 => 是Mapper阶段输出的 Text, IntWritable
Reducer阶段的计算逻辑:
1.接受Mapper端的数据
2.将相同单词所有的Value进行累加
3.将累加后的单词作为Key 单词数和作为Value 写出
KEYOUT, VALUEOUT: 表示Reducer阶段经过逻辑计算后输出的结果
KEYOUT => 单词 => Text
VALUEOUT => 总和 => IntWritable
*/
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer
/**
* reduce方法中可以定义用户的聚合的处理逻辑
*
* @param key 一个单词 hello
* @param values 类型:Iterable
* @param context 上下文对象 可以连接Mapper和Reducer
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable oneValue : values) {
int intValue = oneValue.get(); // intValue => 1
sum += intValue;
}
// TODO 累加完成 需要将数据写出到HDFS或其他地方
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(sum);
context.write(key,outValue);
}
}
WordCount.java
package com.shujia.mr.compress;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionCodec;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineTextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 配置压缩
// 开启Map端的压缩
// conf.setBoolean("mapreduce.map.output.compress",true);
// conf.setClass("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec", BZip2Codec.class, CompressionCodec.class);
// 最终输出的结果数据也是压缩格式的
// 使用的是默认的压缩方式
// conf.setClass("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec", BZip2Codec.class, CompressionCodec.class);
// conf.setBoolean("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress",true);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "My First Word Count ");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job,true);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job,BZip2Codec.class);
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/wordcount");
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/wordCount");
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(job.getConfiguration());
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
/*
未压缩之前:
Map-Reduce Framework
Combine input records=0
Combine output records=0
Reduce input groups=6
Reduce shuffle bytes=253665804 <=
Reduce input records=23317464
Reduce output records=6
Spilled Records=23317464
Shuffled Maps =6
Failed Shuffles=0
Merged Map outputs=6
GC time elapsed (ms)=0
Total committed heap usage (bytes)=2072510464
压缩之后
Combine input records=0
Combine output records=0
Reduce input groups=6
Reduce shuffle bytes=492749 <=
Reduce input records=23317464
Reduce output records=6
Spilled Records=23317464
Shuffled Maps =6
Failed Shuffles=0
Merged Map outputs=6
GC time elapsed (ms)=18
*/
// 合理设置Reduce数量
// 按照Hadoop默认情况下 Reduce处理的数据量每256M 自动生成一个 Reduce
// 一般优化是 按照数据量除以 128M 手动参数给定一个 reduce
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
注意:
要在MapReduce作业中压缩输出,你可以在作业配置过程中设置相关属性,或者使用FileOutputFormat提供的便捷方法。
1. 在作业配置过程中设置属性:
在你的作业配置代码中,可以使用`Configuration`对象来设置压缩相关的属性。具体来说,你可以将`mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress`属性设为`true`来启用输出压缩,然后将`mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec`属性设置为你打算使用的压缩编解码器的类名。
例如,假设你想使用Gzip压缩格式,你可以这样设置属性:
```java
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress", "true");
conf.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec", "org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec");
这样,在你的MapReduce作业中,输出文件将会以Gzip格式进行压缩。
使用FileOutputFormat提供的便捷方法: 另一种方案是在FileOutputFormat中使用更便捷的方法来设置压缩相关的属性。你可以使用FileOutputFormat的静态方法setCompressOutput和setOutputCompressorClass来设置输出压缩。 例如,使用Gzip压缩格式,你可以这样设置: import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec;
// 设置输出压缩
FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
// 设置压缩编解码器
FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
这样,在你的MapReduce作业中,输出文件将会以Gzip格式进行压缩。
无论你选择哪种方案,都需要确保你的压缩编解码器类在你的项目中可用,并且与你的Hadoop版本兼容。
package com.shujia.mr.compress;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionCodec; import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionCodecFactory; import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionInputStream;
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadCompressFile { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 1.对于压缩文件不能直接进行打开查看
// 2.对于压缩文件需要使用对应的方式进行读取数据 -> FileSystem进行读取 -> 会根据文件的后缀自动识别压缩格式
String inputPath = "hadoop/data/out/wordCount/part-r-00001.bz2";
String outputPath = "hadoop/data/out/wordCount/1.txt";
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 读取压缩文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(inputPath);
// 根据文件类型选择具体使用哪个解压类
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(conf).getCodec(new Path(inputPath));
// 将字节流转换成可以解压缩的IO流
CompressionInputStream inputStream = codec.createInputStream(fileInputStream);
// 创建输出流将数据写出
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(outputPath));
// 将输入流和输出流进行连接
IOUtils.copyBytes(inputStream,fileOutputStream,conf);
IOUtils.closeStream(inputStream);
IOUtils.closeStream(fileOutputStream);
}
}
它使用了Hadoop的Configuration对象和相关的类来完成读取压缩文件的操作。
首先,通过Configuration对象创建一个压缩文件的输入流FileInputStream,并指定要读取的压缩文件的路径inputPath。
接下来,使用CompressionCodecFactory类来根据压缩文件的后缀自动选择合适的解压缩类CompressionCodec。在这个示例中,使用了getCodec方法来获取与压缩文件对应的解压缩类。
然后,通过解压缩类的createInputStream方法将字节流fileInputStream转换为可以解压缩的输入流CompressionInputStream。
接着,创建一个输出流FileOutputStream,用于将解压缩后的数据写入到输出文件outputPath中。
最后,通过IOUtils类的copyBytes方法将输入流和输出流连接起来,实现数据的解压缩和写入。最后,记得关闭输入流和输出流。
请注意,这段代码假设你已经安装了适当的压缩编解码器,并且压缩文件的路径和输出文件的路径是正确的。你可以根据需要修改这些路径以适应你的实际情况。
## Combiner 预聚合操作
Combiner预聚合操作是在MapReduce作业的Map阶段之后,在数据传输到Reduce阶段之前进行的一个可选操作。它的目的是在Map阶段输出的键值对进行一些局部聚合操作,以减少传输给Reduce阶段的数据量,从而提高作业的性能。
在Map阶段,每个Mapper会将输入数据映射为一系列键值对。如果启用了Combiner预聚合操作,那么在将这些键值对传输给Reduce阶段之前,会先对每个Mapper的输出进行局部聚合。
Combiner操作是在Mapper节点上执行的,它将相同键的值进行合并,从而减少传输的数据量。这样,Reduce节点在接收到数据之前,就已经进行了一定程度的聚合操作。
Combiner预聚合操作的使用可以通过调用job.setCombinerClass()方法来指定一个实现了Reducer接口的类作为Combine函数。这个Combine函数会在Map阶段之后,在数据传输给Reduce阶段之前被调用。
使用Combiner预聚合操作可以有效地减少数据传输量,减轻Reduce阶段的负担,提高作业的性能。尤其在一些计算密集型的作业中,Combiner操作可以显著减少数据的传输和处理时间。
需要注意的是,Combiner操作必须满足关联性和交换性的要求,即对于相同键的多个值,Combiner操作的结果必须与Reduce操作的结果相同。因此,在使用Combiner预聚合操作时,需要确保Combiner函数的实现满足这些要求。
怎么操作
要编写一个Combiner预聚合操作的实现,需要创建一个类来实现Reducer接口,并重写其reduce()方法。下面是一个示例:
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
public class MyCombineReducer extends Reducer
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
sum += value.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个名为MyCombinerReducer的类,它继承了Reducer类,并指定了输入键值对的类型(Text和IntWritable)和输出键值对的类型(Text和IntWritable)。
在reduce()方法中,我们对相同键的值进行求和操作,并将结果写入上下文(Context)中。在这个示例中,我们使用了一个IntWritable对象来保存求和的结果。
要在MapReduce作业中启用Combiner预聚合操作,可以在作业配置中调用job.setCombinerClass()方法,并指定MyCombineReducer类作为Combiner函数的实现,如下所示:
Job job = new Job();
// ...
job.setCombinerClass(MyCombineReducer.class);
// ...
通过这样的设置,MapReduce作业会在Map阶段之后,在数据传输给Reduce阶段之前,使用MyCombineReducer类中的reduce()方法进行预聚合操作。
需要注意的是,Combiner操作的输入和输出类型必须与Map阶段的输出类型相同。在这个示例中,Map阶段的输出类型是Text和IntWritable,因此Combiner操作的输入和输出类型也是Text和IntWritable。
根据具体的需求,你可以根据自己的数据和聚合逻辑来编写自定义的Combiner函数。
实例
WordCountMapper.java
```
package com.shujia.mr.combiner;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
自定义Mapper类需要继承Mapper 该Mapper需要给定4个泛型
public class Mapper
KEYIN: 输入数据的Key类型 存储的数据是 偏移量(指数据读取的开始位置也表示之前读取到哪个长度) 使用长整型 Java中为Long
由于Hadoop内部实现了一套自己的数据表达式方式 Writable ,所有的Java类型都有其对应的 Hadoop数据类型
Java中为Long => LongWritable
VALUEIN: 表示输入数据的Value类型 存储的是一行数据 Java中为String 字符串
Java中为String 字符串 => Text
输出的数据类型需要根据 计算逻辑推算得到
Mapper阶段的计算逻辑:
1.拿到一行字符串数据Value
2.将Value进行按空格切分
3.将切分后的数据遍历得到每个单词
4.对每个单词作为Key 拼接一个 Value 1
根据上述的逻辑:
KEYOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Key类型 => 单词 => 字符串 => Java中使用String => Hadoop中使用 Text
VALUEOUT: 表示经过Mapper计算后得到的结果的Value类型 => 1 => 整型 => Java中使用 int => IntWritable
注意:导入类时不要选错包 org.apache.hadoop.io 包路径下
*/
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper
/**
* 需要重写map方法,在该方法中可以实现Mapper端的计算逻辑
*
* @param key 输入的数据的Key => 偏移量 => 读取数据的长度位置
* @param value 读取的一行数据 : hello world
* @param context 表示会话 用于连接Mapper端和Reducer端 形成一个整体
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper
// Text是Hadoop中的数据类型 提供了哪些方法?
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
// TODO 遍历每个单词
for (String word : words) {
// TODO 需要将 word 作为Key 1作为Value写出结果
// 1. word => String类型 要求输出类型为 Text 如何转换 ?
// 2. 1 => int类型 要求输出类型为 IntWritable 如何转换 ?
// 3. 当前Map方法没有返回值 如何将数据写出?
Text outKey = new Text(word);
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(1);
// 通过调用 context.write 可以将数据写出到Reducer阶段
context.write(outKey, outValue);
}
}
}
```
WordCountReducer.java
```
package com.shujia.mr.combiner;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
Reducer阶段主要是对数据进行做汇总操作
自定义Reducer类需要继承Reducer抽象类 需要提供四个泛型
public class Reducer
KEYIN, VALUEIN: 输入数据的Key和Value的类型 => 是Mapper阶段输出的 Text, IntWritable
Reducer阶段的计算逻辑:
1.接受Mapper端的数据
2.将相同单词所有的Value进行累加
3.将累加后的单词作为Key 单词数和作为Value 写出
KEYOUT, VALUEOUT: 表示Reducer阶段经过逻辑计算后输出的结果
KEYOUT => 单词 => Text
VALUEOUT => 总和 => IntWritable
*/
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer
/**
* reduce方法中可以定义用户的聚合的处理逻辑
*
* @param key 一个单词 hello
* @param values 类型:Iterable
* @param context 上下文对象 可以连接Mapper和Reducer
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable oneValue : values) {
int intValue = oneValue.get(); // intValue => 1
sum += intValue;
}
// TODO 累加完成 需要将数据写出到HDFS或其他地方
IntWritable outValue = new IntWritable(sum);
context.write(key,outValue);
}
}
```
WordCount.java
```
package com.shujia.mr.combiner;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*
执行jar包的命令
hadoop jar hadoop-1.0.jar com.shujia.mr.wordcount.WordCount
*/
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "Combiner");
// 需要设置当前Jar包的入口类
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
// 设置当前Job的Mapper类和Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 设置Mapper端的输出KeyValue类型及最终输出的KeyValue类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/wordcount");
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/wordCount");
// 要求给定的类继承于 Reducer Class cls
// 当前CombinerClass设置的类的reduce方法 会在Mapper阶段进行执行 => 称为预聚合过程
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(job.getConfiguration());
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
// TODO 如果输入路径不存在 需要抛出异常
throw new Exception("给定的文件路径不存在");
// TODO 作业:如果文件不存在,那么可以从 传入参数中进行获取 args 中获取
// hadoop jar XXXX.jar 类路径 /input /output
}
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
// 设置ReduceTask的数量
job.setNumReduceTasks(3);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交Job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
/*
TODO: 普通操作下执行日志:
MapTask日志
File System Counters
// 当前MapTask中读取的字节数
FILE: Number of bytes read=101241231
// 当前MapTask中写出的字节数
FILE: Number of bytes written=135691654
Map-Reduce Framework
// 当前MapTask中读取的条数
Map input records=3204636
// 输出的行数
Map output records=6220766
// 输出的字节数
Map output bytes=55232870
Map output materialized bytes=67674420
Input split bytes=126
// Combine input 条数为 0
Combine input records=0
Spilled Records=12441532
// 垃圾回收线程执行的时间
GC time elapsed (ms)=19
Total committed heap usage (bytes)=681574400
ReduceTask执行日志
// shuffle过程的字节数 => 在集群中通过网络IO读取
Reduce shuffle bytes=58014018
// 输入的总条数 5274000
Reduce input records=5274000
Reduce output records=2
Spilled Records=5274000
Shuffled Maps =3
Failed Shuffles=0
Merged Map outputs=3
GC time elapsed (ms)=0
Total committed heap usage (bytes)=1476919296
*/
/*
TODO 添加Combiner操作之后日志执行情况:
输入的数据条数
Map input records=3204636
输出的数据条数
Map output records=6220766
Map output bytes=55232870
Map output materialized bytes=142
Input split bytes=126
// Combine输入的数据条数和map输出的数据条数一致
Combine input records=6220766
// Combine聚合之后输出的数据条数为12条
Combine output records=12
Spilled Records=24
Failed Shuffles=0
Merged Map outputs=0
GC time elapsed (ms)=18
Reducer执行日志:
Reduce端shuffle过程发送的数据128字节
Reduce shuffle bytes=128
// 接收到数据条数为10条
Reduce input records=10
// 最终有2条数据写出
Reduce output records=2
Spilled Records=10
Shuffled Maps =3
Failed Shuffles=0
Merged Map outputs=3
GC time elapsed (ms)=0
*/
// TODO 结论:通过比较Shuffle过程的字节数 可以看出Combine 预聚合操作可以减少shuffle过程中的IO操作 提高整体执行效率
}
}
```
## 增大环形缓冲区
```
在MapReduce中,Shuffle阶段是将Mapper的输出按照Key进行排序并传递给Reducer的过程。这个过程中,涉及到磁盘IO操作和内存缓冲区的使用。
缓冲区大小对MapReduce程序的执行效率有一定影响。原则上,缓冲区越大,磁盘IO的次数越少,执行速度就越快。这是因为较大的缓冲区可以容纳更多的数据,减少了磁盘IO的次数,从而提高了数据传输的效率。
在MapReduce中,缓冲区的大小可以通过参数`mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb`进行调整。默认值为100MB。您可以根据实际情况和资源配置来调整这个值。
需要注意的是,调整缓冲区大小需要综合考虑以下因素:
1. 可用内存:较大的缓冲区需要占用更多的内存资源。确保您的集群有足够的可用内存来支持增大缓冲区的操作。
2. 数据规模:如果处理的数据规模较小,增大缓冲区可能不会带来明显的性能提升。相反,如果处理的数据规模较大,增大缓冲区可能会显著减少磁盘IO次数,提高执行速度。
3. 磁盘空间:较大的缓冲区会占用更多的磁盘空间来存储临时数据。确保您的集群有足够的磁盘空间来支持增大缓冲区的操作。
综上所述,调整缓冲区大小需要综合考虑资源配置、数据规模和性能需求等因素。可以根据实际情况进行适当的调整,以达到最佳的执行效率。
```
**怎么调整缓冲区大小**
要调整MapReduce中的缓冲区大小,您可以通过以下两种方法来实现:
在MapReduce作业的配置中设置参数:您可以在提交MapReduce作业时,通过配置文件或命令行参数来设置缓冲区大小。对于参数mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb来说,默认值是100MB。您可以将其调整为更大或更小的值,以适应您的需求。例如,如果您希望增大缓冲区大小为200MB,可以在提交作业时使用以下命令:
hadoop jar your_job_jar.jar your_main_class -Dmapreduce.task.io.sort.mb=200
在MapReduce程序中使用Configuration对象设置参数:如果您在编写MapReduce程序时使用了Configuration对象来设置作业配置,您可以在程序中直接设置缓冲区大小。以下是一个示例代码片段,演示如何设置缓冲区大小为200MB:
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
public class YourMapReduceJob {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.setInt("mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb", 200);
// 设置其他作业配置参数
// ...
// 提交作业
// ...
}
}
无论您选择哪种方法,都需要确保您的集群有足够的内存资源来支持增大缓冲区的操作,并且根据实际情况进行适当的调整。同时,还需要注意磁盘空间的使用情况,以确保有足够的空间存储临时数据。
## MapJoin(减少reducer阶段)
MapJoinMapper.java
```
package com.shujia.mr.mapjoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MapJoinMapper extends Mapper
HashMap
/**
* Called once at the beginning of the task.
* 当前setup函数 会在每个MapTask任务一开始启动时会执行一次
*/
@Override
protected void setup(Mapper
System.out.println("setup函数被执行...");
// TODO: 1.当该函数被执行时,可以读取所有的总分数据 hadoop/data/out/count/part-r-00000
// 通过IO流读取 => BufferReader中的readLine方法
// 当数据在HDFS中存储时,就不能使用Java的IO流读取HDFS数据
// 所以需要使用 FileSystem对象中的open方法 创建一个IO流对象 之后再对数据进行包装
// 问题:如何获取FileSystem对象? => context对象中的配置类创建
URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();
for (URI cacheFile : cacheFiles) {
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
FSDataInputStream fsDataInputStream = fileSystem.open(new Path(cacheFile));
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fsDataInputStream));
idAndScore = new HashMap<>();
String line = "";
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
// 1500100003 359
String[] split = line.split("\t");
if (split.length == 2){
String id = split[0];
String score = split[1];
// TODO:2.创建一个容器,将id和score存入,之后再从Map方法中对该容器进行调用 通过ID获取其成绩
// System.out.println("line:"+line);
// 添加数据
idAndScore.put(id,score);
}
}
}
}
/*
需求:
将Student数据和Score数据按照ID进行关联 过程中使用MapJoin
由于Student数据较大 选择将总分数据先读取到内存中
*/
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper
String oneLine = value.toString();
String[] split = oneLine.split(",");
if (split.length == 5){
String id = split[0]; // 1500100001,施笑槐,22,女,文科六班
String scoreOrDefault = idAndScore.getOrDefault(id, "0");
context.write(new Text(id+","+split[1]+","+split[2]+","+split[3]+","+split[4]+","+scoreOrDefault),NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
```
MapJoinDriver .java
```
package com.shujia.mr.mapjoin;
import com.shujia.mr.filter.score.more450.FilterDriver;
import com.shujia.mr.filter.score.more450.FilterMapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MapJoinDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(MapJoinDriver.class);
job.setJobName("MapJoin");
job.setMapperClass(MapJoinMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// 最终输出的就是Mapper端输出的
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// 设置输入输出路径
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
// 将MapJoin小表加载的路径在Driver端进行定义
job.addCacheFile(new Path("hadoop/data/out/count/part-r-00000").toUri());
Path inputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/students.txt");
// Path inputPath = new Path("/data/reduce_join");
if (!fileSystem.exists(inputPath)) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(inputPath+"路径不存在");
}
Path outputPath = new Path("hadoop/data/out/mapjoin");
// Path outputPath = new Path("/data/out/count");
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)){
fileSystem.delete(outputPath,true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath);
// 提交job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
```
在这种情况下,文件"hadoop/data/out/count/part-r-00000"被添加到分布式缓存中。当作业运行时,这个文件将在集群中的所有节点上可用。在Hadoop中执行Map-Side Join时,通常会使用分布式缓存将较小的数据集(“小表"或"小输入”)加载到每个节点的内存中,以提高性能。
要在MapReduce作业中访问此文件,您可以在Mapper或Reducer类中使用以下代码:
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 获取缓存文件的路径
Path[] cacheFiles = context.getLocalCacheFiles();
if (cacheFiles != null && cacheFiles.length > 0) {
// 读取文件的内容
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(cacheFiles[0].toString()));
// 根据需要使用文件的内容
// ...
// 关闭文件读取器
reader.close();
}
}
在Mapper或Reducer类的setup方法中,您可以使用context.getLocalCacheFiles()获取分布式缓存中文件的路径。在这种情况下,您添加的文件将在cacheFiles[0]处可用。然后,您可以读取和处理文件的内容。
请注意,setup方法在处理任何记录之前每个任务只调用一次,因此它是初始化任何资源或从分布式缓存加载数据的好地方。
## MapReduce优化
MapReduce优化主要是为了提升执行的效率,针对数据处理过程中以下几个方面来对MapReduce过程进行调整:
> 数据输入
> Map阶段
> IO传输
> Reduce阶段
**数据输入**
问题:**合并小文件**:因为大量小文件会产生大量的Map任务,而任务的装载比较耗
时,从而导致MR运行较慢
解决方案:
1.修改输入类为CombineTextInputFormat,MR默认的输入类下,会根据小文件数量创建切片,并且一个切片对应一个MapTask,这样产生大量MapTask,处理效率极其低下
2.在读取计算前,对**小文件进行合并**
**Map阶段**
问题:多次溢写会产生多个溢写文件,并且最终需要合并成一个结果文件
解决方案:
1.增大触发**spill的内存上限**,减少spill次数,从而减少磁盘IO
io.sort.mb:环形缓存区大小,默认为100MB
sort.spill.percent:默认溢出率为(80%)
2.不影响业务逻辑前提下,先进行Combine处理,减少I/O
一般来说增大环形缓存区即可,增加不多就不必增加
**IO阶段**
问题:大量的网络传输,会降低MR执行效率
解决方案:
1.采用数据压缩的方式,减少网络IO的时间
2.通过**Combine**或者提前过滤数据减少数据传输量
3.适当备份,因为备份多可以本地化生成map任务
**Reduce阶段**
问题:执行效率慢
解决方案:
1.合理设置Reduce数量
2.使用MapJoin规避使用Reduce,减少shuffle
3.使Key分配均匀,避免数据倾斜的产生
## Mapper类和Reducer类的源码方法
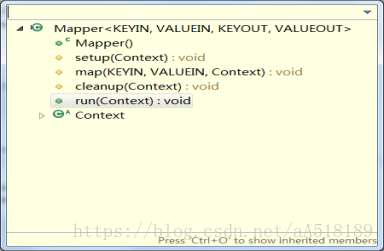
基类Mapper类和Reducer类中都是只包含四个方法:setup方法,cleanup方法,run方法,map方法。
其方法的调用方式是在run方法中,如下所示:
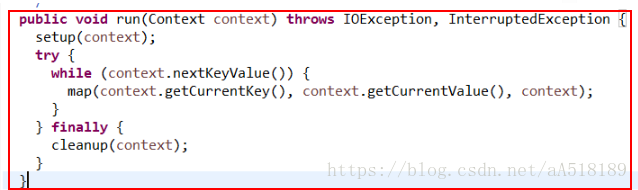
可以看出,在run方法中调用了上面的三个方法:setup方法,map方法,cleanup方法。
对于每个maptask和reducetask来说,都是先调用run()方法,因此根据源代码中run()方法的结构可以看出,不管是map任务还是reduce任务,程序都要经过如下几个阶段:调用run()方法-->调用setup(context)方法-->循环执行map()或reduce()方法-->最后调用cleanup(context)方法
其中setup方法和cleanup方法默认是不做任何操作,且它们只被执行一次。但是setup方法一般会在map函数之前执行一些准备工作,如作业的一些配置信息等;cleanup方法则是在map方法运行完之后最后执行 的,该方法是完成一些结尾清理的工作,如:资源释放等。如果需要做一些配置和清理的工作,需要在Mapper/Reducer的子类中进行重写来实现相应的功能。map方法会在对应的子类中重新实现,就是我们自定义的map方法。该方法在一个while循环里面,表明该方法是执行很多次的。run方法就是每个maptask调用的方法。
hadoop中的MapReduce框架里已经预定义了相关的接口,其中如Mapper类下的方法setup()和cleanup()。
setup(),此方法被MapReduce框架仅且执行一次,在执行Map任务前,进行相关变量或者资源的集中初始化工作。若是将资源初始化工作放在方法map()中,导致Mapper任务在解析每一行输入时都会进行资源初始化工作,导致重复,程序运行效率不高!
cleanup(),此方法被MapReduce框架仅且执行一次,在执行完毕Map任务后,进行相关变量或资源的释放工作。若是将释放资源工作放入方法map()中,也会导致Mapper任务在解析、处理每一行文本后释放资源,而且在下一行文本解析前还要重复初始化,导致反复重复,程序运行效率不高!
所以,建议资源初始化及释放工作,分别放入方法setup()和cleanup()中进行。
apper或Reducer类中使用以下代码:
```java
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 获取缓存文件的路径
Path[] cacheFiles = context.getLocalCacheFiles();
if (cacheFiles != null && cacheFiles.length > 0) {
// 读取文件的内容
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(cacheFiles[0].toString()));
// 根据需要使用文件的内容
// ...
// 关闭文件读取器
reader.close();
}
}
```
在Mapper或Reducer类的`setup`方法中,您可以使用`context.getLocalCacheFiles()`获取分布式缓存中文件的路径。在这种情况下,您添加的文件将在`cacheFiles[0]`处可用。然后,您可以读取和处理文件的内容。
请注意,`setup`方法在处理任何记录之前每个任务只调用一次,因此它是初始化任何资源或从分布式缓存加载数据的好地方。
MapReduce优化
MapReduce优化主要是为了提升执行的效率,针对数据处理过程中以下几个方面来对MapReduce过程进行调整:
数据输入 Map阶段 IO传输 Reduce阶段
数据输入 问题:合并小文件:因为大量小文件会产生大量的Map任务,而任务的装载比较耗 时,从而导致MR运行较慢 解决方案: 1.修改输入类为CombineTextInputFormat,MR默认的输入类下,会根据小文件数量创建切片,并且一个切片对应一个MapTask,这样产生大量MapTask,处理效率极其低下 2.在读取计算前,对小文件进行合并
Map阶段 问题:多次溢写会产生多个溢写文件,并且最终需要合并成一个结果文件 解决方案: 1.增大触发spill的内存上限,减少spill次数,从而减少磁盘IO io.sort.mb:环形缓存区大小,默认为100MB sort.spill.percent:默认溢出率为(80%) 2.不影响业务逻辑前提下,先进行Combine处理,减少I/O
一般来说增大环形缓存区即可,增加不多就不必增加
IO阶段 问题:大量的网络传输,会降低MR执行效率 解决方案: 1.采用数据压缩的方式,减少网络IO的时间 2.通过Combine或者提前过滤数据减少数据传输量 3.适当备份,因为备份多可以本地化生成map任务
Reduce阶段 问题:执行效率慢 解决方案: 1.合理设置Reduce数量 2.使用MapJoin规避使用Reduce,减少shuffle 3.使Key分配均匀,避免数据倾斜的产生
Mapper类和Reducer类的源码方法
基类Mapper类和Reducer类中都是只包含四个方法:setup方法,cleanup方法,run方法,map方法。
其方法的调用方式是在run方法中,如下所示:
可以看出,在run方法中调用了上面的三个方法:setup方法,map方法,cleanup方法。
对于每个maptask和reducetask来说,都是先调用run()方法,因此根据源代码中run()方法的结构可以看出,不管是map任务还是reduce任务,程序都要经过如下几个阶段:调用run()方法–>调用setup(context)方法–>循环执行map()或reduce()方法–>最后调用cleanup(context)方法
其中setup方法和cleanup方法默认是不做任何操作,且它们只被执行一次。但是setup方法一般会在map函数之前执行一些准备工作,如作业的一些配置信息等;cleanup方法则是在map方法运行完之后最后执行 的,该方法是完成一些结尾清理的工作,如:资源释放等。如果需要做一些配置和清理的工作,需要在Mapper/Reducer的子类中进行重写来实现相应的功能。map方法会在对应的子类中重新实现,就是我们自定义的map方法。该方法在一个while循环里面,表明该方法是执行很多次的。run方法就是每个maptask调用的方法。
hadoop中的MapReduce框架里已经预定义了相关的接口,其中如Mapper类下的方法setup()和cleanup()。
setup(),此方法被MapReduce框架仅且执行一次,在执行Map任务前,进行相关变量或者资源的集中初始化工作。若是将资源初始化工作放在方法map()中,导致Mapper任务在解析每一行输入时都会进行资源初始化工作,导致重复,程序运行效率不高!
cleanup(),此方法被MapReduce框架仅且执行一次,在执行完毕Map任务后,进行相关变量或资源的释放工作。若是将释放资源工作放入方法map()中,也会导致Mapper任务在解析、处理每一行文本后释放资源,而且在下一行文本解析前还要重复初始化,导致反复重复,程序运行效率不高! 所以,建议资源初始化及释放工作,分别放入方法setup()和cleanup()中进行。
精彩文章

发表评论